Grab Homework With Python and Telegram Bot
So I’m taking a programming paradigms course this semester and the homework will be published every Friday on a webpage. It’s kinda boring to check this webpage manually every Friday to grab the homework. Meanwhile, I noticed that the webpage is quite simple and easy to be scraped using python. So…why not? Spending a few hours to write a small piece of code to grab the homework automatically sounds great.
All these efforts just to grab your homework? Why?
- It’s fun!
- It’s cool and that’s what we CS student do 😉
- It’s a great way to apply what I’ve learned to solve real world problem.
- It’s a typical use case for web scraping and the code can be easily adapted to other scenarios. Have you ever applied for something (for example: a Visa for traveling in another country), and eagerly waited for the result to be published online? Have you ever manually refreshed the webpage again and again just in hope that the result would pop up? Well, let Python do all the work for you so that you can
Netflix and Chillspend your time on something more interesting.
Web scrapping with python
Study the webpage
The homework links are located in this webpage. Right click and choose Inspect to view the HTML code of this site.
The homework links are located in a table element.
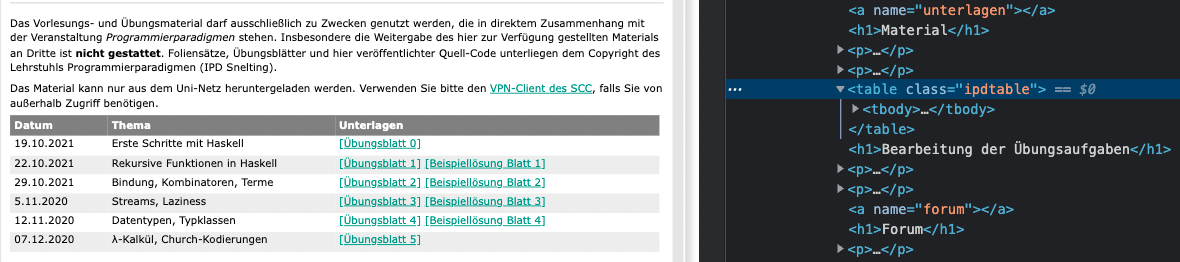
And then we can see all the links of homework are located in the <a> (or anchor) element.
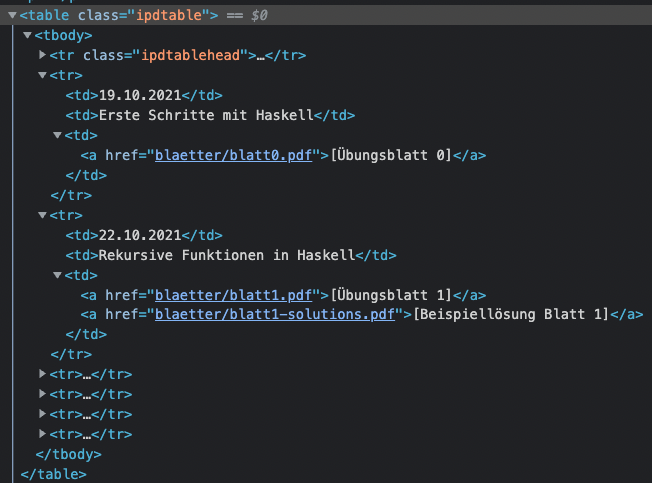
All right, time to write some code to get all the links.
Write the code
Import libraries:
import bs4, requests, os
import urllib.parse as ul
bs4 for beautiful soup, os to read and write files, requests to get HTML data and urllib.parse to make URL more friendly.
Get the HTML of this page:
def get_page(url):
page = requests.get(url)
page.raise_for_status()
return page.text
Get homework table and extract homework links from anchor element:
def get_table(page):
#Store content of the page
soup = bs4.BeautifulSoup(page, 'lxml')
#get table which contains uebungsmaterial
table = soup.find_all('table')[1]
return table
#Get links of howework in the table
def get_uebung_links(table):
links = []
#get links from anchor elements in the table
for row in table.find_all('tr')[1:]:
try:
for anchor in row.find_all('td')[2].find_all('a'):
links.append(anchor['href'])
except ValueError:
continue #ignore blank/empty row
return links
Now we get the links of all the homework given but we only need the newly added homework not all the homework. My way to solve this problem is to create a local file to store the result of last scrape and compare with the fresh scrape. If difference found, call telegram bot and send the link.
Store result of last scrape as local file and compare
#stored html file of lecture page from last scrape
page_storage = "page_storage.html"
def compare(page_fresh, page_storage):
fresh_links = get_uebung_links(get_table(page_fresh))
if os.path.isfile("./" + page_storage):
with open(page_storage, "r", newline='') as f:
storage = f.read()
storage_links = get_uebung_links(get_table(storage))
f.close()
if storage_links != fresh_links:
with open(page_storage, "w", newline='') as f:
f.write(page_fresh)
f.close()
call_bot(get_difference(fresh_links, storage_links), token, chat_id)
else:
print('You are up to date.')
else:
with open(page_storage, "w", newline='') as f:
f.write(page_fresh)
f.close()
call_bot(combine_url_with_links(url, fresh_links), token, chat_id)
If the local file does not exist, it means this is the first scrape so that we create and save the html data to the local file and send all the links through telegram bot.
If the local file exists, compare it with the fresh screaped page and when difference is found, send the difference through telegram bot and update the local file. If there’s no difference, we’re up to date.
There are some help functions in the code above. I’ll go through them in the content below.
Setting up Telegram Bot
- Use BotFather to create new bot accounts and manage your existing bots.
- Get bot token from BotFather.
- Get telegram chat id / group id (depends on where you want to use the bot).
If you want to use the bot with your personal account, add the bot with your personal account and send a dummy message to the bot and check this url (remember to replace <YourBOTToken> with your bot token):
https://api.telegram.org/bot<YourBOTToken>/getUpdates
Look for the chat object and you should find your chat id there. It’s basicly the same if you want to use the bot in a group. The difference is you need to add the bot to the group first and then interact with it and get the group id using the url above.
You can then send message to your account / group through this bot using this url:
"https://api.telegram.org/bot" + token + "/sendMessage?chat_id=" + chat_id + "&text={}".format(parsed_updates)
token is your bot token given by BotFather. chat_id is your account/group id. parsed_updates is the message you want to send.
Help functions
# Get what has been changed in the table.
# Return added item list and deleted item list
def get_difference(fresh_links, storage_links):
added = []
for item in fresh_links:
if item not in storage_links:
added.append(url + item)
return added
# Prepare result text for telegram bot
def form_resultText(added_list):
length = len(added_list)
if length == 0:
return "No update"
else:
updates = "Added:\n"
for item in added_list[:(length - 1)]:
updates += item + "\n"
updates += added_list[length - 1]
return updates
def make_updates_url_friendly(updates):
return ul.quote_plus(updates)
# Build telegram bot request url
def build_telegram_bot_requestUrl(token, chat_id, parsedUpdates):
return "https://api.telegram.org/bot" + token + "/sendMessage?chat_id=" + chat_id + "&text={}".format(parsed_updates)
# URL of lecture programming paradigmen
url = "https://pp.ipd.kit.edu/lehre/WS202122/paradigmen/uebung/"
# Combine base url with homework link (homework links don't contain main url originally)
def combine_url_with_links(url, link_list):
url_links = []
for link in link_list:
url_links.append(url + link)
return url_links
Call the bot
def call_bot(added_list, token, chat_id):
parsed_updates = make_updates_url_friendly(form_result_text(added_list))
requests.get(build_telegram_bot_request_url(token, chat_id, parsed_updates))
Finally, we need to call compare function to start the scrape:
compare(get_page(url),page_storage)
Scheduling
Crontab is a job scheduler on Ubuntu. Since the assignment is always due on Friday, I set the scheduler to run at minute 15 past every hour from 14 through 18 on Friday.
$ crontab -e
15 14-18 * * 5 /path/to/python3 /path/to/updater.py >> /path/to/cron.log 2>&1
Future improvement
-
Scrape website with authentication system
-
Downloading file automatically
-
Dealing with VPN requirement